What is a Switching Power Supply and How Does It Work?
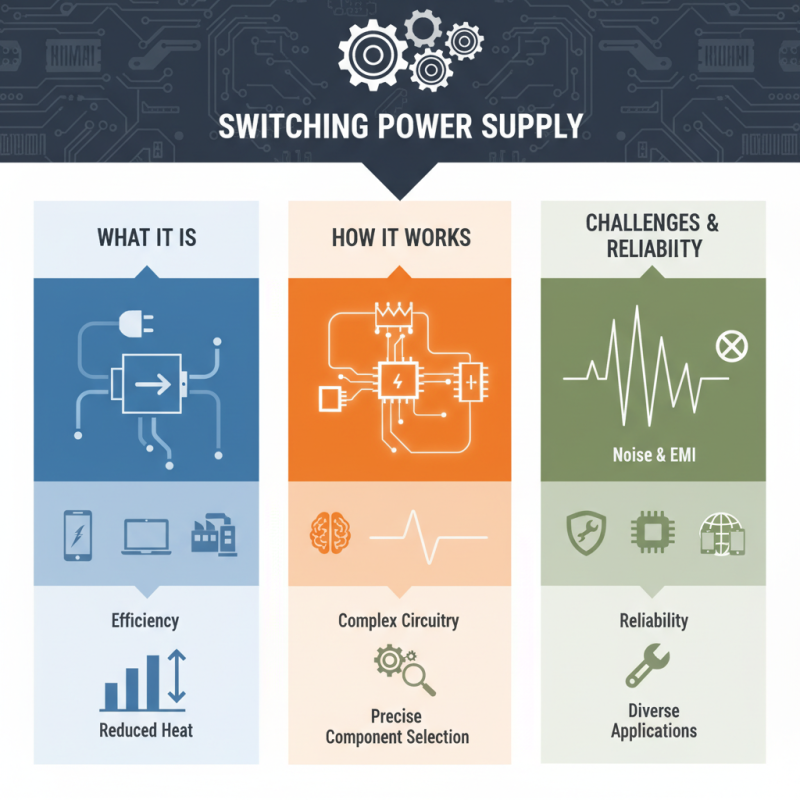
A Switching Power Supply is a crucial component in modern electronics. It efficiently converts electrical power from one voltage level to another. Unlike traditional power supplies, it uses high-frequency switching to control energy transfer. This design leads to improved efficiency and reduced heat output.
Switching Power Supplies are found in various devices. Laptops, smartphones, and industrial machines all rely on them. They provide stable power and save energy. However, this technology is not without challenges. Noise and electromagnetic interference can be issues that require attention.
Understanding how a Switching Power Supply works is essential. It involves complex circuitry and precise component selection. While these devices offer many advantages, potential drawbacks must not be overlooked. Evaluating their performance in different applications is key to ensuring reliability.
Definition of Switching Power Supply and Its Importance
A switching power supply (SPS) is a crucial component in modern electronics. It converts electrical power efficiently. This technology reduces energy waste and enhances device performance. According to industry reports, SPS can achieve efficiencies over 90%. This is significant in a world striving for energy conservation.
The importance of switching power supplies extends beyond efficiency. They are vital for compact designs. Many electronic devices require a lightweight and small power source. Switching supplies meet these needs. They allow manufacturers to design more innovative products. Their ability to handle varying input voltages is also notable. This adaptability is essential in today’s diverse power environments.
However, not everything is perfect. The design of SPS can sometimes introduce electromagnetic interference. This can disrupt nearby electronic equipment. Engineers must carefully consider layout and shielding. Balancing efficiency and noise reduction is challenging. Continuous improvements in technology aim to address these issues, highlighting the ongoing evolution of switching power supplies.
Basic Components of a Switching Power Supply
A switching power supply (SPS) is an essential component in many electronic devices. Understanding its basic components is crucial for those working in electronics. At the heart of an SPS is the input rectifier, which converts AC voltage into DC. This process is vital for consistency in power supply, especially in devices that require stable operation.
Next, the high-frequency switch, usually a transistor, plays a pivotal role. It alternates the DC into high-frequency AC. This high-frequency conversion allows for the use of smaller transformers, thus reducing overall weight and size of the power supply. The output transformer then steps down the voltage to the desired level, crucial for the functionality of various devices.
**Tip:** When designing or troubleshooting a switching power supply, always check the feedback loop. A well-functioning feedback loop ensures voltage regulation and responsiveness.
The final component is the output rectifier, which converts the high-frequency AC back into usable DC. While this system is efficient, some users overlook the importance of heat management. Without adequate cooling, components can overheat, reducing lifespan significantly.
**Tip:** Regularly assess component temperatures under load. This practice can help identify potential failures before they occur.
Switching power supplies play a critical role in modern electronics. Their ability to handle a variety of voltage levels while maintaining efficiency is unmatched. However, ensure to consider each component's role thoroughly in your projects.
How a Switching Power Supply Converts Voltage
A switching power supply is a critical component in modern electronics. It efficiently converts voltage from one level to another. This conversion process is essential for devices like computers and smartphones.
The heart of a switching power supply is its switching regulator. It rapidly switches the input voltage on and off. This action creates pulses of voltage. These pulses are then transformed and smoothed into a stable output. The switching frequency is typically high, allowing for smaller components.
One intriguing detail is the feedback mechanism involved. It adjusts the output voltage in real-time. However, this system can sometimes introduce noise. If not managed well, it leads to performance issues. Balancing efficiency and stability can be challenging. Understanding these intricacies helps improve design and function.
Advantages of Using Switching Power Supplies
Switching power supplies are becoming the standard in various applications due to their unique advantages. One of the primary benefits is their higher efficiency compared to linear power supplies. Reports indicate that switching power supplies can achieve efficiencies between 80% to over 90%. This means less energy is wasted as heat. Lower energy loss translates to reduced operational costs, especially in large-scale applications like data centers.
Another advantage is their compact size. Due to their high efficiency, switching power supplies can be designed to be smaller and lighter. This is crucial for portable devices and consumer electronics. Data suggests that a typical switching power supply can be up to 70% smaller than a comparable linear supply. However, this smaller form factor can sometimes limit thermal management features, leading to overheating risks if not properly designed.
Moreover, switching power supplies offer better voltage regulation under varying load conditions. This is important in critical applications where maintaining a consistent output is essential. However, the complexity of their design can introduce issues such as electromagnetic interference (EMI). Proper shielding and filtering are necessary to mitigate this problem. It's essential to weigh these benefits against potential drawbacks when choosing the right power supply for a specific application.
Common Applications of Switching Power Supplies
Switching power supplies are widely used in various applications. They provide a stable power source for electronic devices. Commonly found in computers, they convert AC power to DC with high efficiency. This efficiency is crucial for devices that require consistent voltage. They are lighter and more compact than traditional linear power supplies.
Telecommunications also benefit from switching power supplies. They support base stations and routers, ensuring reliable communication. The demand for compact and efficient power solutions drives innovation in this area. However, not all designs are perfect. Some can produce electrical noise, which might affect sensitive equipment.
In industrial applications, switching power supplies power machinery and automation systems. Their compact nature allows for easy integration into manufacturing processes. Yet, designers must be cautious of heat dissipation. Inadequate thermal management can lead to failures. Understanding these challenges is important for engineers when creating reliable systems.